United States Army Air Defense Activities
(page 113)
UNITED STATES ARMY AIR DEFENSE SCHOOL
Figure 113. Hinman Hall, US Army Air Defense School.
HISTORY
The US Army Air Defense School (fig 113) traces its lineage back to the Artillery
Corps for instruction (later named the Coast Artillery School) established at Fortress
Monroe, Virginia, on 5 April 1824.
By March 1942, the antiaircraft portion of the Coast Artillery School had
outgrown the facilities at Fort Monroe. This portion of the Coast Artillery School
was then transferred to Camp Davis, North Carolina, and was established as the
Antiaircraft Artillery School coincident with the activation of the Antiaircraft
Command, Army Ground Forces, an outgrowth of the Office of the Chief of Coast
Artillery. In October 1944, the School moved to Fort Bliss, Texas.
The period following 1944 witnessed outstanding technological progress in air
defense artillery weapons and a rapid growth in the responsibilities of the Air
Defense School. Technologically, weapons progressed from the 40-mm, 90-mm, and
120-mm guns through the Skysweeper, Nike Ajar, and Nike Hercules, to Hawk and
Improved Nike Hercules.
On 1 July 1957, after several changes in its name, the School was designated
as the US Army Air Defense School.
US ARMY AIR DEFENSE SCHOOL
The School (fig 114) provides all required career and specialist school
education and training for selected students, both officer and enlisted, of
all components of the Army. Emphasis in all instruction is on the art of
leadership. The School also provides career and specialist school education
and training for selected students of other US military services, military
students from friendly nations, civilian personnel employed by US Government
agencies, and personnel of industrial or research organizations under contract
to the US Government.
ASSISTANT COMMANDANT
The assistant commandant supervises the operation of the US Army Air Defense
School, acts for the commandant as directed, and assumes the duties and
responsibilities of the commandant during his absence.
DEPUTY ASSISTANT COMMANDANT
The deputy assistant commandant assists in the supervision of the operation
of the US Army Air Defense School and acts for the assistant commandant as directed.
SENIOR USAF-USMC REPRESENTATIVES
The senior US Air Force representative develops and presents instruction on
US Air Force subjects; performs liaison between US Air Force agencies and the
School and USAADCEN agencies: and advises the commandant, staff, and faculty on
organization, functions, doctrine, procedures, and capabilities of the US Air Force.
The senior US Marine Corps representative develops and presents instruction
on US Navy and US Marine Corps subjects, performs liaison between US Marine Corps
and US Navy agencies and the School and USAADCEN agencies, and exercises supervision
over US Marine Corps personnel stationed at Fort Bliss.
BUDGET AND MANAGEMENT OFFICE
The chief of the Budget and Management Office acts as the principal staff
element for budgeting, internal control of funds, management engineering, manpower
control, and statistical reporting and analysis. The Office serves as School
coordinating agency for Project TRIM--Army Cost Reduction Program.
ORGANIZATION OF US ARMY AIR DEFENSE SCHOOL
AND
MISSIONS OF PRINCIPAL OFFICES
Figure 114. Air Defense School organization.
SECRETARY
The secretary serves as the administrative executive for the School.
He supports the operation of the School with administrative military personnel,
message center, automatic data processing, student actions, academic records,
bookstore, library civilian personnel, and special prolects services.
He also supervises the School safety program and acts as the School contact
point for senior foreign liaison representatives.
SCHOOL SUPPORT COMMAND
Commanding Officer, School Support Command, commands all units and personnel
of the School Support Command. The School Support Command provides administrative,
logistical, and training (nonacademic) support for US students and the School staff
and faculty; provides administrative and logistical support for foreign military
students; provides logistical and security services in support of School operations;
and exercises summary and special courtsmartial jurisdiction Over assigned and
attached US Army enlisted personnel.
DIRECTOR OF INSTRUCTION
The director of instruction directs the academic department,
coordinates their instruction operation,
supports the conduct of School operation,
prepares plans for the academic requirements, and provides television
Instructional facilities for the School. He maintains liaison with, provides
guidance and support to, and acts as the School's point of contact for
the US Army Human Research Unit.
DIRECTOR OF DOCTRINE REVIEW AND TRAINING LITERATURE
The director of doctrine review and training literature develops equipment
training plans and devices; acts as the combat development staff element of the
School: prepares and keeps current air defense artillery Army-wide, applicatory-type
training literature; provides staff supervision for preparation of School instructional
publications; develops and revises air defense artillery and fire distribution system
maintenance MOS evaluation test materials; studies and recommends revision of MOS
specificiations for enlisted, warrant officer, and officer personnel; develops
and revises a resycling policy for air defense artillery advanced individual
training; assists in the production of air defense training films; and provides
training support for the exchange officer at the School of Artillery, Manorbier,
United Kingdom.
COMMAND AND STAFF DEPARTMENT
The director of the Command and Staff Department is responsible for conducting
instsuction in command and staff matters of air defense, combined arms, nuclear
weapons, and missile science; participates in the evolution and formulation of
doctrine; participates in the preparation, review, and revision of Army-wide
training literature, training films, and MOS evaluation tests; supports air
defense instruction at other service schools; monitors School troops demonstrations
and field exercises; and sponsors senior officer courses of instruction.
MISSILE ELECTRONICS AND FIRE DISTRIBUTION SYSTEMS DEPARTMENT
The director of the Missile Electronics and Fire Distribution Systems Department
is responsible for conducting instruction in electronics, digital technology, and fire
distribution systems; participates in the evolution and formulation of doctrine:
participates in the preparerion. review and revision of Army-wide training literature,
training films, and MOS evaluation rests; and maintains equipment.
LOW ALTITUTE MISSILE DEPARTMENT
The director of the Low Altitude Missile Department is responsible for conducting
insrmction in the low-altinde air defense weapon systems and associated subjects:
participates in the evolution and formulation of doctrine; participates in the
preparation, review, and revision of Army-wide training literature, training films,
and MOS evaluation tests; and maintains equipment.
HIGH ALTITUDE MISSILE DEPARTMENT
The director of the Nigh Altitude Missile Department is responsible for conducting
instruction in the operational Nike missile systems, their associated radar signal
simulators, alternate battery and defense acquisition radars, and electronics warfare;
participates in the evolution and formulation of doctrine; participates in the
preparation, review, and revision of Army-wide training literature, training films,
and MOS evaluation tests; and maintain. equipment.
NONRESIDENT INSTRUCTION DEPARTMENT
The director of the Nonresident Instruction Department prepares and administers
air defense elbensioa courses, prepares and provides instructional material for
Army Reserve Components, and distributes School-published material to authorized agencies.
ACADEMIC ACCOMPLISHMENTS
Since the initiation of air defense artillery instruction in 19(2 the Air Defense
School has graduated more than 195,000 students. During World War II, more than
60,000 irdividUals were graduated from courses conducted at the School.
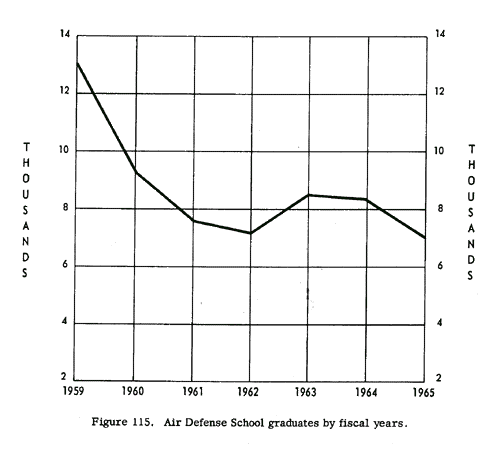
During FY 65, the School conducted 57 courses (US and non-US) for 313
graduated classes. Courses varied in length from 1 to 59 weeks. Included
in the 7,088 graduates during FY 65 were 2,014 from other countries. In terms
of air defense artillery skills, the graduates included:
Figure 115. Air Defense School graduates by fiscal years.
COMBAT DEVELOPMENTS COMMAND AIR DEFENSE AGENCY
The US Army Combat Developments Command Air Defense Agency (USACDCADA)
was organized as a class II activity at Fort Bliss on 1 July 1962. This agency
is part of the US Army Combat Developments Command (USACDC) established in the
1961 reorganization of the Army. USACDCADA is responsible to the Commanding General,
USACDC, through the US Army Combat Developments Command, Combined Arms Group,
Fort Leavenworth, and is one of 10 branch or combat functional agencies of the
Combined Arms Group.
USACDCADA is charged with determining how air defense artillery units should
be organized and equipped and how they should fight. These tasks are accomplished
by studying future requirements and preparing tables of organization and equipment
for all air defense artillery units, qualitative materiel development objectives,
qualitative materiel requirements, small development requirements for air defense
artillery equipment, and doctrinal field manuals on air defense artillery employment.
USACDCADA represents the user in the development cycle, participates in development
of the maintenance package, and reviews equipment technical manuals.
The development of organizational concepts, materiel requirements, and doctrine
requires close coordination with many agencies. USACDCADA maintains liaison with the
Communications-Electronics Agency, USACDC, for the use of frequencies; with the Aviation
Agency; USACDC, for the use of airspace; and with other combined arms agencies as the
plans and programs become more finalized. Liaison is also maintained with major oversea
commands and Allied nations to facilitate a fully coordinated national and international
air and space defense program and to take advantage of technical developments made by
others. Close coordinadon with the ALT Defense School, Air Defense Board, and other
agencies at Fort Bliss permits taking advantage of the knowledge of air defense
artillery personnel assigned to these agencies. USACDCADA keeps tbese agencies
informed of new developments so that future requirements for training mechanics,
operators, and supervisors for future air defense artillery systems can be planned.
US ARMY AIR DEFENSE BOARD
The US Army Air Defense Board, a class n: activity at Fort Bliss, is a
subordinate command of the US Army Test and Evaluation Command. Aberdeen
Proving Ornmd, Maryland. The Board's mission is to plan aad conduct service rests,
evaluations, check tests, and confirmatory tests. It participates in planning and
conducting engineering tests: planning, supervising, and monitoring Mop tests; and
providing guidance during development of air defense artillery equipment.
Included in the Board's general field of responsibility are air defense artillery
weapon systems, fire distribution systems, air defense artillery ECM and ECCM equipment
and devices, and rmdeaIdemolltion munitioes. It furnishes guidance to Department of
the Army in selecting training devices, preparing training literature, determining
maintenance packages, and conducting in-process reviews during equipment development.
The Board works with the contractors and Army agencies concerned to insure that
equipment meets military characteristics and user requirements. .Close liaison is
maintained with the Navy, Marine Corps, and Air Force and with Unfted Kingdom and
Canadian standardization representatives on air defense artillery items of mutual
interest.
The Board is organized into three divisions to accomplish its responsibilities.
The Missile Systems Test Division is responsible for test research and development
pertaining to surface-to-air missile systems, predicted-fire weapons, target drones,
nuclear warheads, and nuclear demolition munitions. The Electronics Systems Test
Division is responsible for matters pertaining to fire distribution systems, radars,
ECM and BCCM components, IFF devices, engine generators, and simulators. The Support
Division is responsible for gathering and reducing test data and providing general
support for Board test activities.
US ARMY AIR DEFENSE HUMAN RESEARCH UNIT
The US Army Air Defense Human Research Unit is a military organization responsible
for providing military support and guidance to contract agencies engaged in human
factors research in air defense. The support and guidance is furnished to the
collocated Human Resources Research Office (HUMRRO) Division No. 5 (Air Defense).
This division is an organization element of the Human Resources Research Office,
a non-Government agency of The George Washington University operating under contract
with Department of the Army.
The research tasks presently being conducted by HUMRRO Division No. 5 are
concerned with:
McGregor Guided Missile Range, organized under the Range Command, US Army Air
Defense Center, Fort Bliss, is the largest inland air defense missile range in the
free world. Located in the State of New Mexico, the range encompasses 1,210 square
miles (684,000 acres).
To meet the increasing need for a larger range and to replace the range
at Red Canyon, New Mexico, McGregor Range was established on 13 July 1956. The
range became operational as a Nike guided missile range in April 1957. From
April 1957 until June 1959, the support of package firings remained the primary
mission of McCregor Range.
Buildup continued and by mid-1959 McGregor Range was capable of supporting
ARADCOM annual service practice units. On 12 August 1959, the first missile was
fired at McGregor Range in support of ARADCOM annual service practice. McCregor
Guided Missile Range has supported all Nike Afax and Nike Hercules training firings
by units from throughout the free world with the exception of a few battalions
conducting service practice on site.
With the activation of the first Hawk battalion in 1959, plans got underway
at McGregor for support of the Hawk training firing missions. The first Hawk missile
was fired there in June 1960.
McGregor Range, in addition to its training mission, has hosted several
outstanding programs under the supervision of the US Army Air Defense Center.
Thousands of United States citizens and citizens of Allied countries have seen
demonstrations of our air defense capabilities. Nearly 10, 000 surface-to-air
missile firing missions have been completed at McGregor Range.
KEEPING ABREAST OF TECBNICAL DEVELOPMENTS
Guided missile materiel is under constant study by manufacturers, tactical
units, technical agencies, the US Army Air Defense Board, Combat Developments
Command Air Defense Agency, and the Air Defense School. Studies are conducted
to detect materiel weaknesses and to improve maintenance and operational procedures.
To assist the School in keeping abreast of the Latest air defense artillery
materiel developments, representatives are stationed at the School of Artillery,
Pembrokeshire, Manorbier, United Kingdom; at the pacific Field Office, Nike X Prolect,
Kwajalefn Atoll, Marshall Islands; and at the Bell Telephone Laboratories,
Whippany, New Jersey.
The close worldng relationship of the School with the Air Defense Board and
Combat Developments Command Air Defense Agency is a contributing factor in keeping
abreast of technical developments. The Air Defense Executive Conference (ADEX)
grew from this relationship .
AIR DEFENSE EXECUTIVE CONFERENCE
The Air Defense Executive Conference was established to create a relaxed,
friendly, end informal atmosphere for exchanging air defense artillery information
and developing a mutual understanding of air defense artillery problems. The conference
consists of monthly meetings of senior members of the four principal oganiurtions at
Fort Bliss who have Merest in air defense matters: the Air Defense School, Air Defense
Board, Combat Developments Command Air Defense Agency, and US Army Training Center,
Air Defense.
To broaden the scope of information exchanged, standing invitations to participate
are extended to other Army agencies closely associated with solving air defense
problems. These include the Deputy Assistant Commanrlaa and Directors, USAADS, and
a representative from the US Army Air Defense Board, US Army Combat Developments
Command Air Defense Agency, US Army Air Defense Center (G3 and G4), US Army Combat
Developments Command Nuclear Group, US Army Air Defense Command(2), US Army Missile
Command, US Army Ordnance Guided Missile School, Human Resources Research Office,
and White Sands Missile Range.
The meetings, conducted at Fort Bliss, are primarily concerned with doctrine,
policy, planning, teeting, training, and future developments, the approach being
at the executive command level.
Army, Fort Bliss, Texas
SEC 125239
If you have comments or suggestions, Send e-mail
to Ed Thelen
Return to Home
go to "Digest", contents
Updated November 5, 1997
(page 114)
(page 115)
(page 116)
(page 117)
Total graduates for each fiscal year since 1959 are indicated in figure 115.
(page 118)
(page 119)
(page 120)
In addition, explorafory studies are being conducted to determine the
desirability of conducting further research in the following fields:
McGREGOR GUIDED MISSILE RANGE
(page 121)